This is a post to counter the Red Team showcase I made that focuses on using Kali Linux to exploit Metaspolitable 2. In this part, we aim to harden, fix, and defend against what we can with the tools at hand.
Agenda will look like this:
- Nessus, Nmap, Qualys scans – baseline image
- Top vulnerability fixes
- Memory and Volatile Data walk through
- Favorite Linux Blue Team Commands
To start, any prudent defense requires knowing what you are defending. Therefore, Nmap and Nessus are the ideal starting points to map the territory and the big obvious holes that exist.
nmap -n -sV 192.168.56.4nmap -n -sV 192.168.56.4
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2020-05-31 12:01 EDT
Nmap scan report for 192.168.56.4
Host is up (0.0013s latency).
Not shown: 977 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp vsftpd 2.3.4
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 4.7p1 Debian 8ubuntu1 (protocol 2.0)
23/tcp open telnet Linux telnetd
25/tcp open smtp Postfix smtpd
53/tcp open domain ISC BIND 9.4.2
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.8 ((Ubuntu) DAV/2)
111/tcp open rpcbind 2 (RPC #100000)
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.X - 4.X (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
445/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.X - 4.X (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
512/tcp open exec netkit-rsh rexecd
513/tcp open login
514/tcp open tcpwrapped
1099/tcp open java-rmi GNU Classpath grmiregistry
1524/tcp open bindshell Metasploitable root shell
2049/tcp open nfs 2-4 (RPC #100003)
2121/tcp open ftp ProFTPD 1.3.1
3306/tcp open mysql MySQL 5.0.51a-3ubuntu5
5432/tcp open postgresql PostgreSQL DB 8.3.0 - 8.3.7
5900/tcp open vnc VNC (protocol 3.3)
6000/tcp open X11 (access denied)
6667/tcp open irc UnrealIRCd
8009/tcp open ajp13 Apache Jserv (Protocol v1.3)
8180/tcp open http Apache Tomcat/Coyote JSP engine 1.1
Service Info: Hosts: metasploitable.localdomain, irc.Metasploitable.LAN; OSs: Unix, Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Here is the Nessus results:
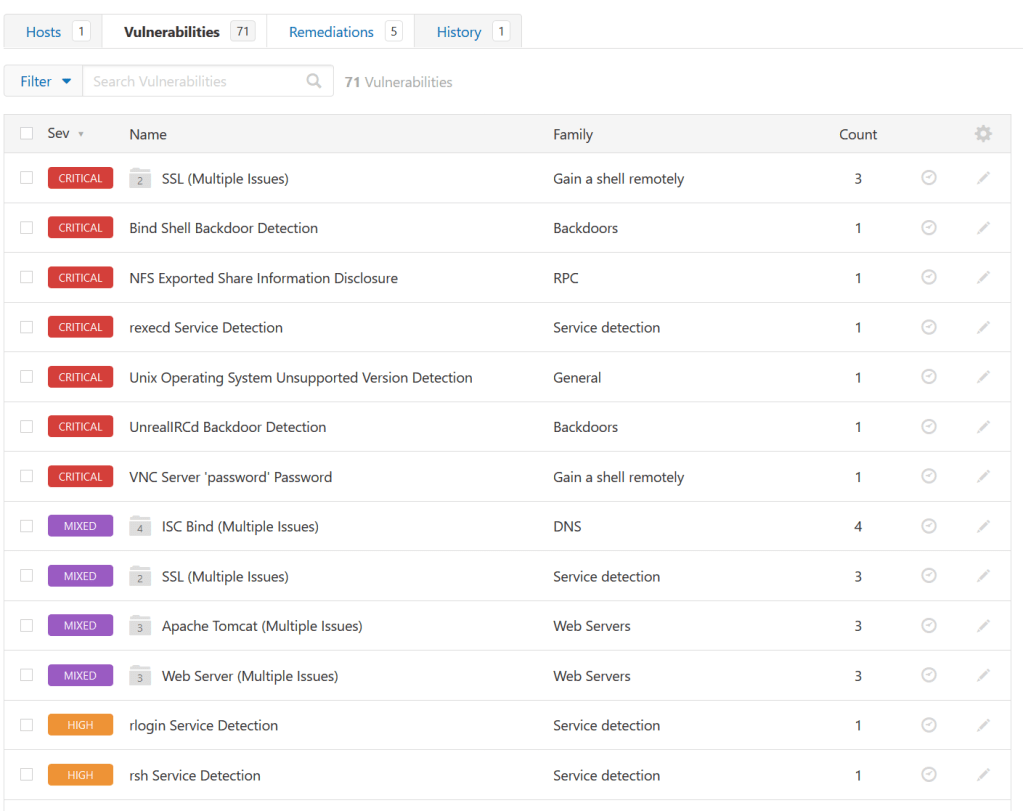
And the Qualys:

Let’s focus on the most critical issues here and see what we can do to fix some of them beyond the obvious “apply a patch”, which we cannot do here.
/etc/inetd.conf
It looks like there are a few items we can address by commenting them out via the /etc/inetd.conf file….
Telnet
Rexecd
Rlogin
Ingreslock Backdoor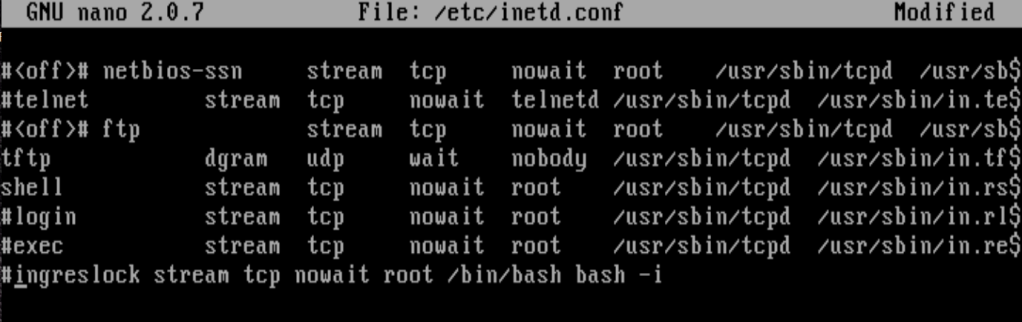
Let’s confirm via Kali Linux.
kali@kali:~$ telnet 192.168.56.4
Trying 192.168.56.4...
telnet: Unable to connect to remote host: Connection refused
rlogin -l root 192.168.56.4
The authenticity of host '192.168.56.4 (192.168.56.4)' can't be established.
Permission denied, please try again.
kali@kali:~$ rsh -l root 192.168.56.4
Permission denied, please try again.
ali@kali:~$ nc 192.168.56.4 1524
(UNKNOWN) [192.168.56.4] 1524 (ingreslock) : Connection refused
IPTables Update
iptables update should also fix a few issues. We can directly block Kali Machines from connecting or just everything except a whitelisted IP.
vsftpd_234 backdoor - drop traffic at port 6200
NFS - drop traffic at port 2049iptables -A INPUT -s IP-ADDRESS -j DROPiptables -A INPUT -s IP-ADDRESS -p tcp --destination-port port_number -j DROPNow when you try to mount the Metasploitable machine via NFS, the root terminal gets frozen and stuck when you directly block Kali Linux.
For the FTP VSFTPD 2.3.4 backdoor, we also need to comment out the /etc/vsftpd.conf with anonymous upload.
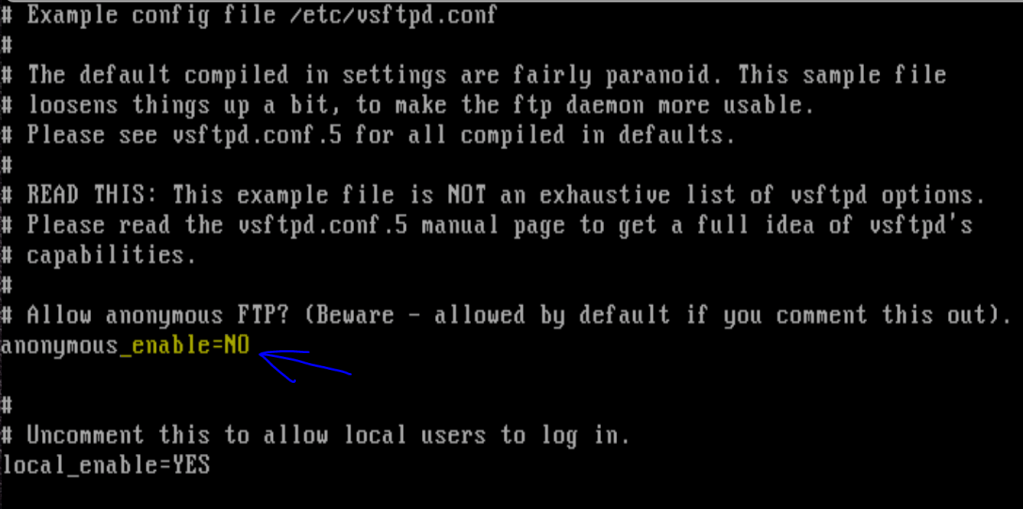
msf5 > use exploit/unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor
msf5 exploit(unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor) > set rhost 192.168.56.4
rhost => 192.168.56.4
msf5 exploit(unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor) > exploit
[-] 192.168.56.4:21 - Exploit failed [unreachable]: Rex::ConnectionRefused The connection was refused by the remote host (192.168.56.4:21).
[*] Exploit completed, but no session was created. Ports 139 and 145 – Samba
We need to comment out the userman script so Metasploitable cannot use the exploit/multi/samba/usermap_script and run it to gain access to the victims machine. Granted, there was a patch released, but we can address it directly.
/etc/samba/smb.conf 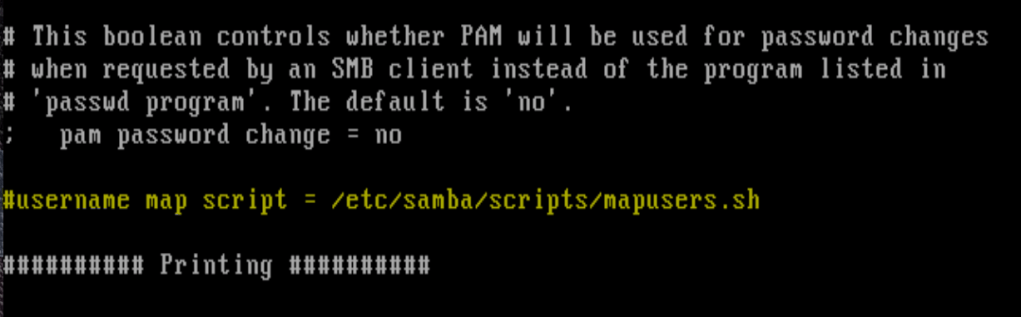
msf5 > use exploit/multi/samba/usermap_script
msf5 exploit(multi/samba/usermap_script) > set rhost 192.168.56.4
rhost => 192.168.56.4
msf5 exploit(multi/samba/usermap_script) > exploit
[*] Started reverse TCP double handler on 192.168.56.6:4444
[*] Exploit completed, but no session was created.
msf5 exploit(multi/samba/usermap_script) >
Port 5432 – PostGresSQL – Directory Change
This is another easy Metasploit exploit that allows the attacker direct access into the Meterpreter shell. PostGresql is set up to write to the default directory – lets change that via:
/etc/postgresql/8.3/main/postgresql.confThe default directory is /var/lib/postgresql/8.3/main so I changed it to ‘/var/lib/postgresql/8.3/datadoom’
data_directory = '/var/lib/postgresql/8.3/datadoom'msf5 > use exploit/linux/postgres/postgres_payload
msf5 exploit(linux/postgres/postgres_payload) > set rhost 192.168.56.6
rhost => 192.168.56.6
msf5 exploit(linux/postgres/postgres_payload) > run
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 192.168.56.6:4444
[-] Connection failed
[*] Exploit completed, but no session was created. What cannot be fixed!
- Port 22 – SSH – Lack of use of passwords > utilize public/private key pairs for authentication instead of passwords.
- Port 3306 – MySQL – Weak passwords > use more complex passwords and or use RSA Keys for mitigation.
- Port 5900 – VNC – Weak passwords > Secure the VNC service with a strong password and or utilize public/private key pairs for authentication instead of passwords.
- Port 6667 – UnrealIRCd – Re-download the software, verify it using the published MD5 / SHA1 checksums, and re-install it.
- Port 8180 – Apache Tomcat -Remove the web server if it is no longer needed. Otherwise, upgrade to a supported version if possible or switch to another server.
I hope this section of this blog gave you an overview of what can and cannot be fixed within Metspolitable 2. Its a tough system to defend but there are some actions that can be taken.
Memory Data Investigation
I include this here as a quick overview of investigating memory of a system after an incident. As we know, artifacts and volatile data can paint a picture of what went wrong and how attackers are being successful.
Things required to start:
- Drive One – This will contain the memory dump – needs to have more memory than the machine that your are collecting
- Drive Two – Forensic tool drive, complied specifically for the drive you are analyzing.
- Trusted source of Linux tools in /media
- USB Mounted drive for data collection at /mount
Process:
- Start a trusted shell (Netcat optional)
- Go to working directory and run script to begin logging.
- Dump memory with Fmem
This was a quick overview, more data here:
https://forensicswiki.xyz/wiki/index.php?title=Tools:Memory_Imaging
Best Blue Team Linux Commands
Unusual Accounts
Look in /etc/passwd for new accounts in sorted list by
UID:
sort –nk3 –t: /etc/passwd | less
Normal accounts will be there, but look for new,
unexpected accounts, especially with UID < 500.
Also, look for unexpected UID 0 accounts:
egrep ‘:0+:’ /etc/passwd
On systems that use multiple authentication methods:
getent passwd | egrep ‘:0+:’
Look for orphaned files, which could be a sign of an
attacker’s temporary account that has been deleted.
find / -nouser -print
Unusual Processes and Services
Look at all running processes:
ps –aux
Get familiar with “normal” processes for the machine.
Look for unusual processes. Focus on processes with
root (UID 0) privileges.
If you spot a process that is unfamiliar, investigate in
more detail using:
lsof –p [pid]
This command shows all files and ports used by the running process. If your machine has it installed, run chkconfig to see which services are enabled at various runlevels:
chkconfig –list
Unusual Scheduled Tasks
Look for cron jobs scheduled by root and any other
UID 0 accounts:
crontab –u root –l
Look for unusual system-wide cron jobs:
cat /etc/crontab
ls /etc/cron.*